Inventory
Host Inventory
| Name | Description | Optional | Valid Value | Starting Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uuid | The UUID. For more information, see Resource Property. | 0.6 | ||
| name | The name. For more information, see Resource Property. | 0.6 | ||
| description | The description. For more information, see Resource Property. | Yes | 0.6 | |
| zoneUuid | The zone UUID. For more information, see Zone. | 0.6 | ||
| clusterUuid | The parent cluster UUID. For more information, see Cluster. | 0.6 | ||
| managementIp | The management IP address. For more information, see Management IP. | 0.6 | ||
| hypervisorType | The hypervisor type. For more information, see Cluster Hypervisor Type. | 0.6 | ||
| state | The state. For more information, see State. |
|
0.6 | |
| status | The status. For more information, see Status. |
|
0.6 | |
| createDate | The creation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 0.6 | ||
| lastOpDate | The last operation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 0.6 | ||
| userTags | The user tags. For more information, see CreateUserTag. | Yes | 0.6 | |
| systemTags | The system tags. For more information, see CreateSystemTag. | Yes | 0.6 | |
| cpuNum | The number of vCPUs. For more information, see CPU Capacity. | 0.6 | ||
| cpuSockets | 0.6 | |||
| availableCpuCapacity | 0.6 | |||
| availableMemoryCapacity | 0.6 | |||
| totalCpuCapacity | 0.6 | |||
| totalMemoryCapacity | 0.6 |
Sample
{
"inventories": {
"availableCpuCapacity": 37,
"availableMemoryCapacity": 4965064704,
"clusterUuid": "967a353c2893409dab9312cf3033a98c",
"cpuNum": 4,
"cpuSockets": 1,
"createDate": "Oct 30, 2017 3:02:06 PM",
"description": "",
"hypervisorType": "KVM",
"lastOpDate": "Oct 31, 2017 10:41:19 AM",
"managementIp": "10.0.146.122",
"name": "Host-1",
"sshPort": 22,
"state": "Enabled",
"status": "Connected",
"totalCpuCapacity": 40,
"totalMemoryCapacity": 8186290176,
"username": "root",
"uuid": "a4049fd68e1b487f8f91786d17ad37e1",
"zoneUuid": "e59b71e99d8a4ea1952b578388b8cd1d"
}
}Host Network Bonding Inventory
| Name | Description | Optional | Valid Value | Starting Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uuid | The UUID. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| hostUuid | The host UUID. | 3.9.0 | ||
| bondingName | The bond name. | 3.9.0 | ||
| mode | The bond mode. | 3.9.0 | ||
| xmitHashPolicy | The hash policy. | 3.9.0 | ||
| miiStatus | The MII status. | 3.9.0 | ||
| mac | The MAC address. | 3.9.0 | ||
| ipAddresses | The IP address. | 3.9.0 | ||
| miimon | The MII monitoring interval. | 3.9.0 | ||
| allSlavesActive | 3.9.0 | |||
| groupBy | Groups rows into subgroups based on values of columns or expressions. This parameter is equivalent to the Group By clause in MySQL, such as groupBy=type. | Yes | 3.9.0 | |
| createDate | The creation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| lastOpDate | The last operation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| userTags | The user tags. For more information, see CreateUserTag. | Yes | 3.9.0 | |
| systemTags | The system tags. For more information, see CreateSystemTag. | Yes | 3.9.0 |
{
"inventories": [
{
"uuid": "2e2226e18e853f20a5791684a1b644c8",
"hostUuid": "903696c585a639bb8049713b98d93437",
"bondingName": "bond0",
"mode": "active-backup 1",
"xmitHashPolicy": "layer2 0",
"miiStatus": "up",
"mac": "ac:1f:6b:93:6c:8c",
"ipAddresses": [
"172.20.0.116/16"
],
"miimon": 100.0,
"allSlavesActive": true,
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"slaves": [
{
"uuid": "17a40aa475cf322494ea82e09066892e",
"hostUuid": "903696c585a639bb8049713b98d93437",
"bondingUuid": "2e2226e18e853f20a5791684a1b644c8",
"interfaceName": "eno1",
"interfaceType": "bondingSlave",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": true,
"carrierActive": true,
"mac": "ac:1f:6b:93:6c:8c",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
},
{
"uuid": "c3716c87b9173cbb8315e7d7f3645bc4",
"hostUuid": "903696c585a639bb8049713b98d93437",
"bondingUuid": "2e2226e18e853f20a5791684a1b644c8",
"interfaceName": "eno2",
"interfaceType": "bondingSlave",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": false,
"carrierActive": false,
"mac": "ac:1f:6b:93:6c:8c",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
}
]
}
]
}Host Network Interface Inventory
| Name | Description | Optional | Valid Value | Starting Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uuid | The UUID. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| hostUuid | The host UUID. | 3.9.0 | ||
| bondingUuid | The bond UUID. | 3.9.0 | ||
| interfaceName | The interface name. | 3.9.0 | ||
| interfaceType | The interface type. Options: nomaster, bridgeSlave, and bondSlave. | 3.9.0 | ||
| speed | The interface speed. | 3.9.0 | ||
| slaveActive | The bond link status. | 3.9.0 | ||
| carrierActive | The physical link status. | 3.9.0 | ||
| ipAddresses | The IP address. | 3.9.0 | ||
| mac | The MAC address. | 3.9.0 | ||
| pciDeviceAddress | The PCI address of the interface. | 3.9.0 | ||
| groupBy | Groups rows into subgroups based on values of columns or expressions. This parameter is equivalent to the Group By clause in MySQL, such as groupBy=type. | Yes | 3.9.0 | |
| createDate | The creation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| lastOpDate | The last operation date. For more information, see Resource Property. | 3.9.0 | ||
| userTags | The user tags. For more information, see CreateUserTag. | Yes | 3.9.0 | |
| systemTags | The system tags. For more information, see CreateSystemTag. | Yes | 3.9.0 |
{
"inventories": [
{
"uuid": "310ca8ce7010363ca7ac83d37373238f",
"hostUuid": "7f8d05522f01397e97f60d84f5ffa2b9",
"bondingUuid": "6fbe88605eed35ba95399687585be3d1",
"interfaceName": "eno1",
"interfaceType": "bondingSlave",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": true,
"carrierActive": true,
"mac": "98:03:9b:00:ea:f1",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
},
{
"uuid": "3213802883d13c72b54c084233c4de2a",
"hostUuid": "7f8d05522f01397e97f60d84f5ffa2b9",
"bondingUuid": "6fbe88605eed35ba95399687585be3d1",
"interfaceName": "eno2",
"interfaceType": "bondingSlave",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": false,
"carrierActive": false,
"mac": "98:03:9b:00:ea:f1",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
},
{
"uuid": "3015b6b0c74d316699ebe09dc60e1001",
"hostUuid": "7f8d05522f01397e97f60d84f5ffa2b9",
"interfaceName": "ens2f0",
"interfaceType": "noMaster",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": true,
"carrierActive": true,
"ipAddresses": [
"169.254.0.115/24"
],
"mac": "98:03:9b:00:ea:f2",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
},
{
"uuid": "e3b513e177a1313a93b32b290643f849",
"hostUuid": "7f8d05522f01397e97f60d84f5ffa2b9",
"interfaceName": "ens2f1",
"interfaceType": "bridgeSlave",
"speed": 1000.0,
"slaveActive": false,
"carrierActive": false,
"mac": "98:03:9b:00:ea:f3",
"createDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM",
"lastOpDate": "Nov 14, 2017 10:20:57 PM"
}
]
}Management IP
- For example, in VMware, the official method to access an ESXi host is to use the vCenter server. In this regard, the management IP address will not be used.
- However, in KVM, ZStack Cloud uses a management IP address to deploy an agent to the Linux operating system.
Management Network
- ZStack Cloud management nodes need to send commands to hosts and other appliances through the management networks. In this regard, the Linux servers that run ZStack Cloud management nodes must be able to access management networks.
- Management networks will be used when it comes to appliance VMs. For the current ZStack Cloud version, the appliance VMs are vRouters or VPC vRouters.
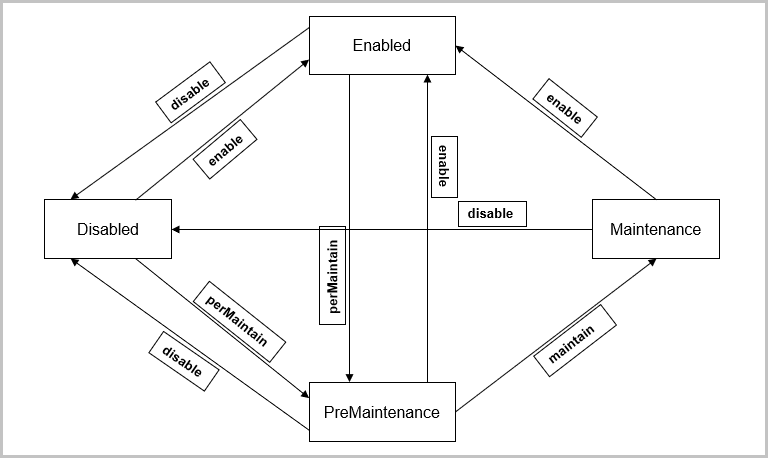
State
- Enabled
Indicates that VM instances can be created and started on, or migrated to the host.
- Disabled:
Indicates that VM instances cannot be created or started on, or migrated to the host.
- Maintenance:
Indicates that the host is in maintenance mode.
 Note:
Note:
PreMaintenance:
Indicates that a host is entering maintenance mode, as shown in Maintenance Mode.
The state transition diagram of a host is shown in Host State Transition Diagram.
Maintenance Mode
- The state of a host is changed to PreMaintenance. At this stage, ZStack Cloud will attempt to migrate all VM instances running on the host to other appropriate hosts. If the migration fails, ZStack Cloud will stop those VM instances.
- After all VM instances are migrated successfully or stopped, ZStack Cloud will change the state of the host to Maintenance. Then, you can perform maintenance jobs on the host.
After the maintenance jobs are completed, you can take a host out of Maintenance mode by placing it to Enabled or Disabled state.
Status
- In KVM, command channels are HTTP connections between ZStack Cloud management nodes and Python agents running on hosts.
- In VMware, command channels are connections between vCenter servers and ESXi hosts.
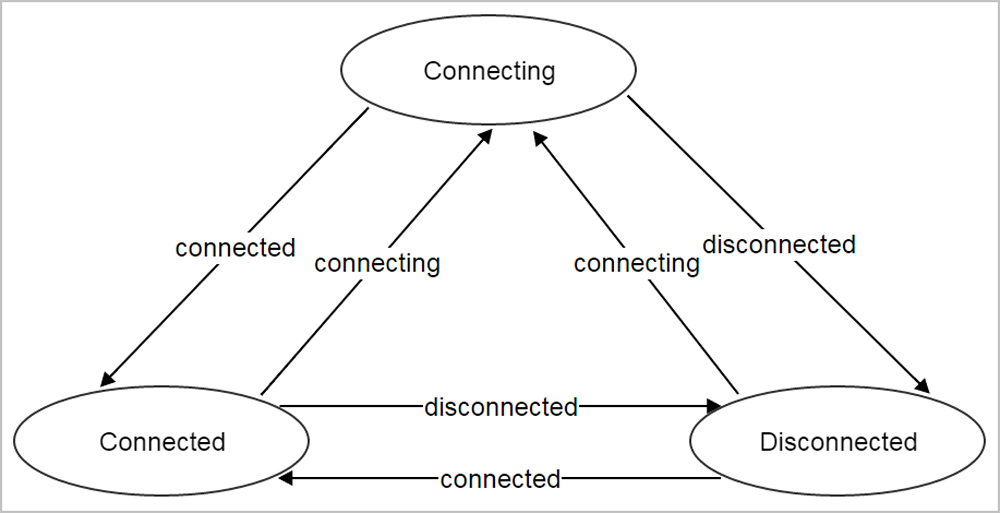
- Connecting:
Indicates that a ZStack Cloud management node is trying to establish a command channel between the node itself and the host. At this stage, you cannot perform any operation on the host.
- Connected:
Indicates that the command channel between a ZStack Cloud management node and the host is successfully established. At this stage, you can perform operations on the host. Only in this status, a host can be used to start or create VM instances.
- Disconnected:
Indicates that the command channel between a ZStack Cloud management node and the host is lost. At this stage, you cannot perform any operation on the host.
When a ZStack Cloud management node starts, a command channel to a host will be established.
- At this stage, the status of the host is Connecting.
- After the command channel is successfully established, the status of the host will be changed to Connected.
- If ZStack Cloud management node fails to establish the command channel, or the command channel is lost at a period of time, the status of the host to which the command channel connects will be changed to Disconnected.
- ZStack Cloud management nodes will periodically send ping commands to hosts to check the health status of command channels. Once a host fails to respond, or a ping command times out, the status of the host will be changed to Disconnected.
The status transition diagram of a host is shown in Diagram for Host Connection Status Transition.
State and Status
The states have no direct relation to the statuses. States represent your decisions on a host, while statuses represent the communication condition of a host.