Port Forwarding
A VPC network uses custom ESX virtual IP addresses (VIPs) or system
ESX VIPs to provide port forwarding service, and has the following features:
- With the port forwarding service, a VPC vRouter can forward the port traffics of a specified public IP address to the port of a corresponding vCenter VM IP address.
- If your public IP addresses are insufficient, you can configure port forwarding for multiple vCenter VM instances by using one IP address and port.
This topic falls into the following parts:
Create a Port Forwarding Rule
The steps of creating a port forwarding rule in a vCenter environment are basically the same as that in a KVM environment.
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose . On the Port Forwarding page, click
Create Port Forwarding. Then, the Create Port
Forwarding page is displayed. On the displayed page, set the parameters. Note:
Note:
 Note:
Note:
- If you choose to create a new VIP to provide port forwarding service, select the public network that you created in the vCenter for Network.
- If you choose to use an existing VIP to provide port forwarding service, select an existing custom ESX VIP or system ESX VIP for VIP.
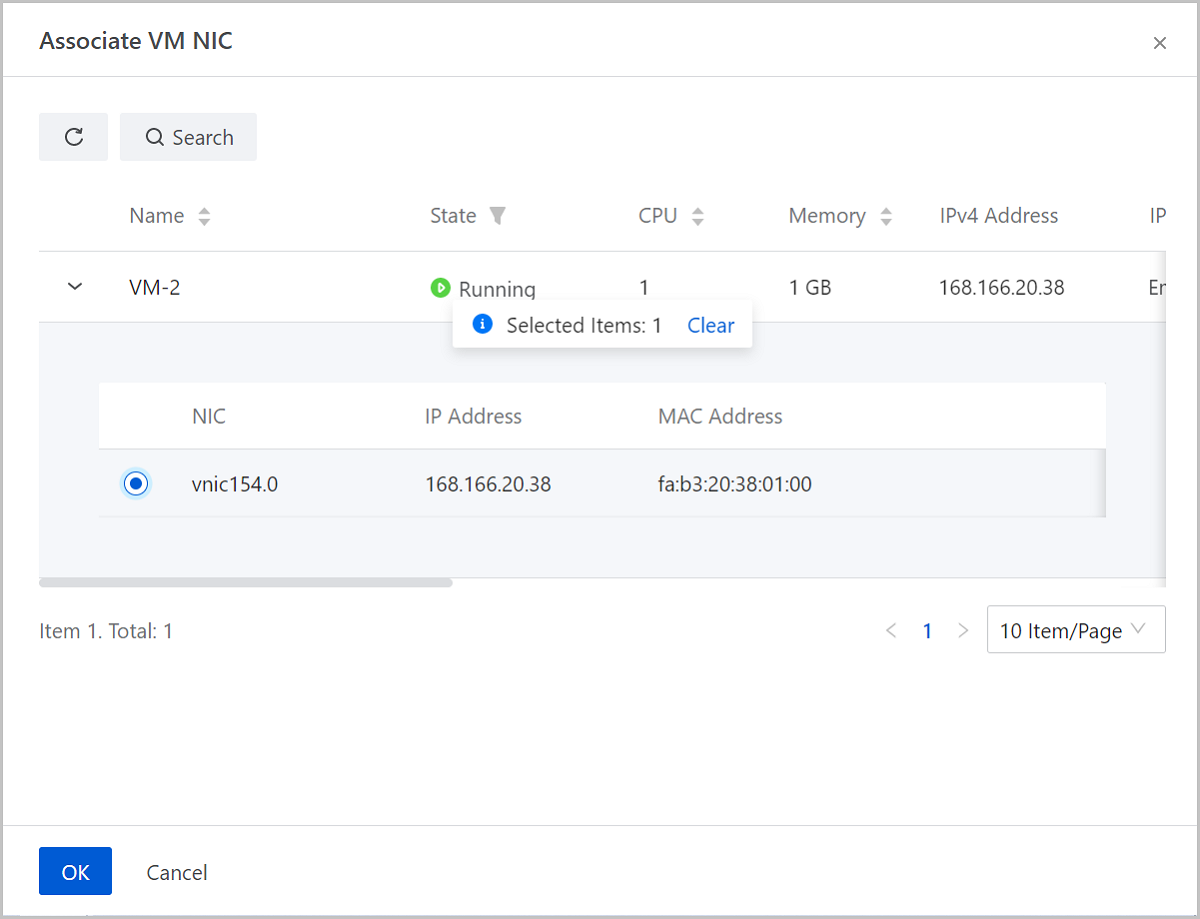
Associate a Port Forwarding Rule with a VM NIC
On the displayed Associate VM NIC page, choose the target VM Instance. On the VM NIC page, select the target vCenter VM NIC, and click OK.
Port Forwarding Actions
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose . Then, the Port Forwarding page is displayed.
The following table lists the actions that you can perform on a Port
Forwarding:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Port Forwarding Rule | Create a new port forwarding rule. |
| Edit Port Forwarding Rule | Edit the name and description of the port forwarding rule. |
| Associate VM NIC | Associate a port forwarding rule with a VM NIC. |
| Disassociate VM NIC | Disassociate a port forwarding rule from a VM NIC. |
| Delete Port Forwarding | Deleting a port forwarding rule also deletes the corresponding port forwarding service. Note that the associated VIP and other services the VIP provides are not affected. |
Notes
- To use port forwarding, make sure that the firewall policy in the VM instances can be accessed by the specified ports.
- When you use a VIP to provide the port forwarding service, make sure that the ports used by the VIP are not duplicated.
- A VIP can provide the port forwarding service to different ports of multiple VM NICs on the same L3 network.
- A VM instance can only use one VIP to provide the port forwarding service.
- When you disassociate a VIP from a VM instance and associate a VM instance again, you can only select the VM NIC on the same L3 network of the VM instance that you disassociated before.
- If you select port range for port forwarding, make sure that the source port range and the VM port range are the same. For example, if you set the range of the source port to 22-80, the port range of the VM instance is also 22-80.