Overview
A virtual router network (vRouter network) mainly uses custom Linux VM instances as route devices. The vRouter VM instances provide many network services, such as DHCP, DNS, SNAT, vRouter table, elastic IP (EIP), port forwarding, load balancing, IPsec tunnel, and security group.
- vRouter image: Encapsulates many network services, and is used only to create vRouters.
- vRouter offering: Defines the resources used by a vRouter, including the CPU, memory, vRouter image, public network, and management network.
- vRouter: Acts as a custom Linux VM instance and provides network services such as DHCP, DNS, SNAT, route table, EIP, port forwarding, load balancing, IPsec tunnel, and security group.
vRouter Network Topology
- Public network
Provides virtual IPs for user VM instances that use EIP, port forwarding, load balancing, and IPsec tunnel. Generally, the public network must be accessible to the Internet.
- Management network
Manages and controls the corresponding physical resources, such as a host, backup storage, and primary storage, of whose resources can be reached by using an IP address.
- Private network
Also known as the business network or the access network and is the internal network used by VM instances.
- You can combine the public network and the management network, while
deploying the private network independently, as shown in Deployment
Mode-1.
Figure 1. Deployment Mode-1 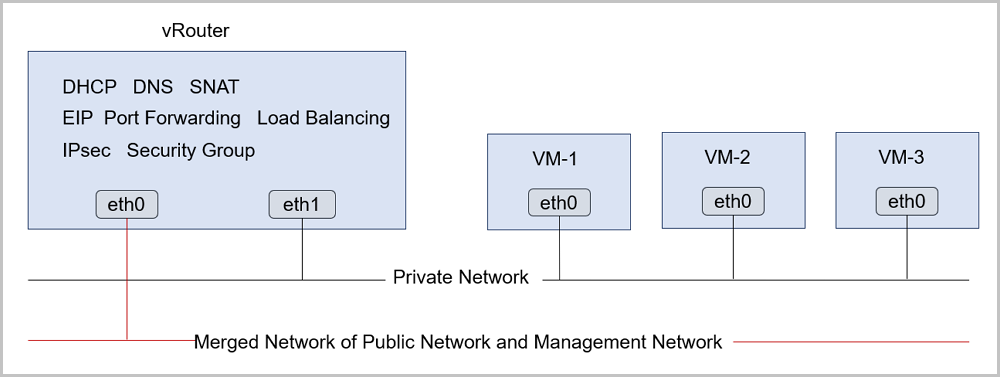
- You can deploy the public network, management network, and private network
separately, as shown in Deployment Mode-2.
Figure 2. Deployment Mode-2 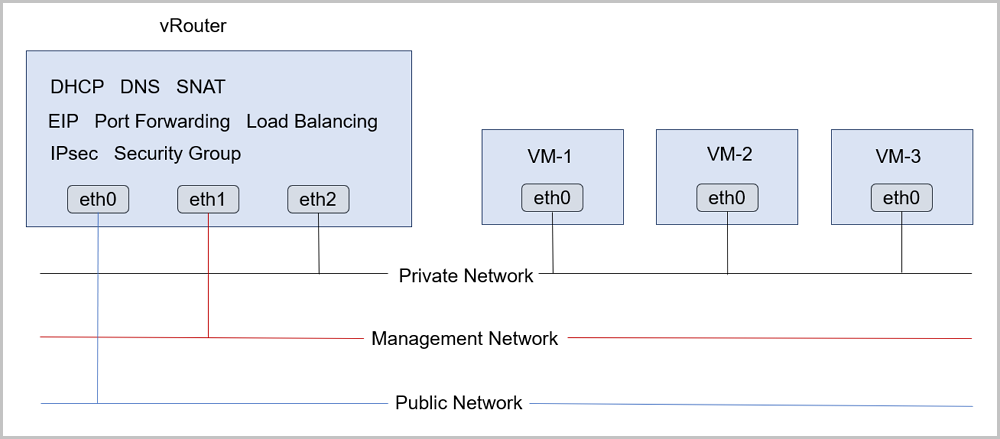
vRouter Network Service
The vRouter VM instances provide a collection of network services, including the DHCP, DNS, SNAT, route table, EIP, port forwarding, load balancing, IPsec tunnel, and security group.
- DHCP
- In a vRouter, the DHCP service is provided by the flat network by default.
- DNS
- A vRouter can act as a DNS server to provide the DNS service.
- The DNS address in a vRouter VM instance is the vRouter IP address. Note that the DNS address that you set is forwarded by the vRouter.
- SNAT
- A vRouter can act as a router to translate the source network address for VM instances.
- VM instances can directly access the Internet by using SNAT.
- We will introduce the vRouter table, security group, EIP, port forwarding, load balancing, and IPsec in specific sections.