EIP
An elastic IP address (EIP) is a method to access a private network through other networks. An EIP converts the IP address of a network into the IP address of another network based on the network address translation (NAT) function.
- The following is an example of a public EIP usage scenario in flat networks, as
shown in EIP
Usage Scenario in Flat Network.
Figure 1. EIP Usage Scenario in Flat Network 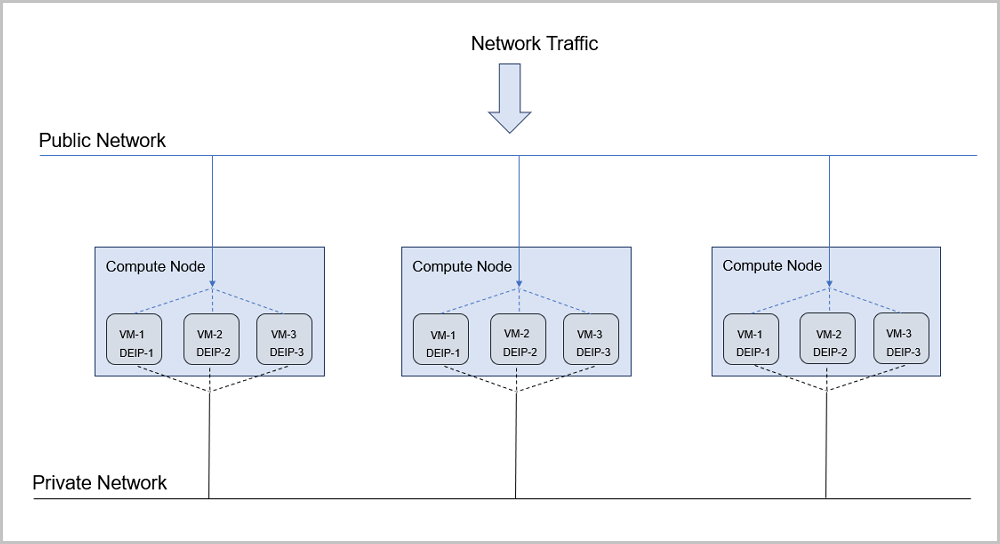
- Public networks can connect to the Internet through firewalls.
- Private networks (flat networks) provide IP addresses for each VM instance in each compute node. Notice that these IP addresses cannot connect to the Internet by default.
- Distributed EIP is deployed on each compute node, and can be bound to public networks or private networks separately.
- The following is an example of an EIP usage scenario in vRouter networks or VPC
networks, as shown in EIP Usage Scenario in vRouter/VPC Network.
Figure 2. EIP Usage Scenario in vRouter/VPC Network 
Definitions related to EIP:
- Public EIP: The EIP service provided by a public VIP created from a public
network.
- An internal private network is an isolated network space, which cannot be directly accessed by the external network. A public EIP can directly associate the access to a public network with the VM IP of an internal private network.
- A public EIP can be attached to or detached from a VM instance dynamically.
- A public EIP can be attached to VM instances created from private
networks, such as flat networks, vRouter networks, and VPC networks.
- The EIP realized by distributed EIP can access flat networks through public networks.
- vRouters or VPC vRouters can be used to access vRouter networks or VPC networks through public networks.
- Flat EIP: The EIP service provided by a flat VIP created from a flat network.
- L3 isolations exist between flat networks of different IP ranges. Therefore, these flat networks cannot be accessed directly. A flat EIP can be used to associate the access to one flat network with the VM IP created from another flat network.
- A flat EIP can be attached to or detached from a VM instance dynamically.
- A flat EIP can be attached to VM instances created from other flat networks.